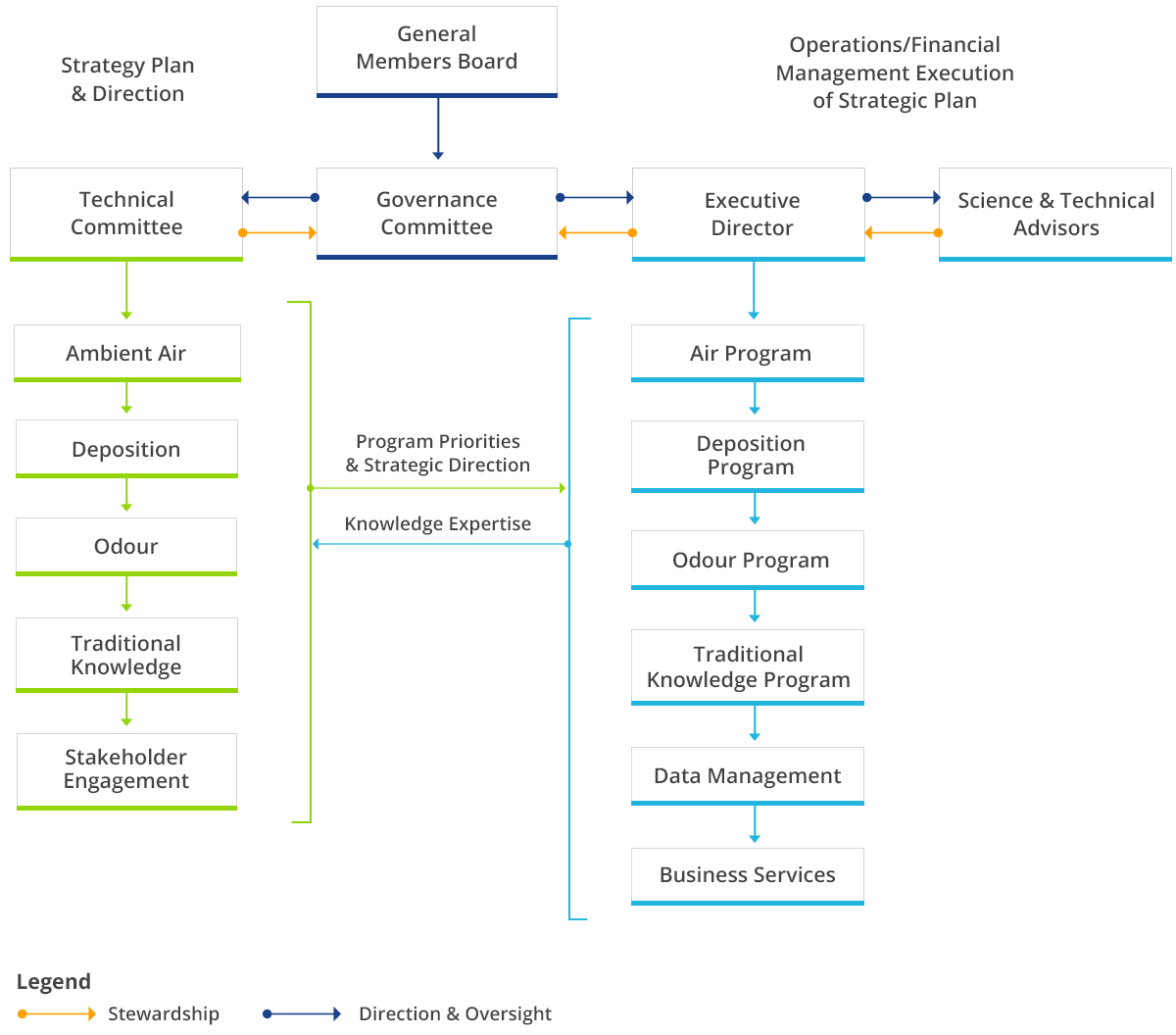
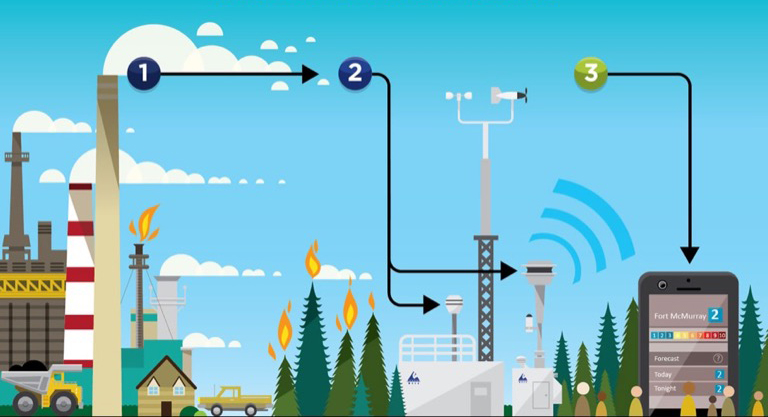
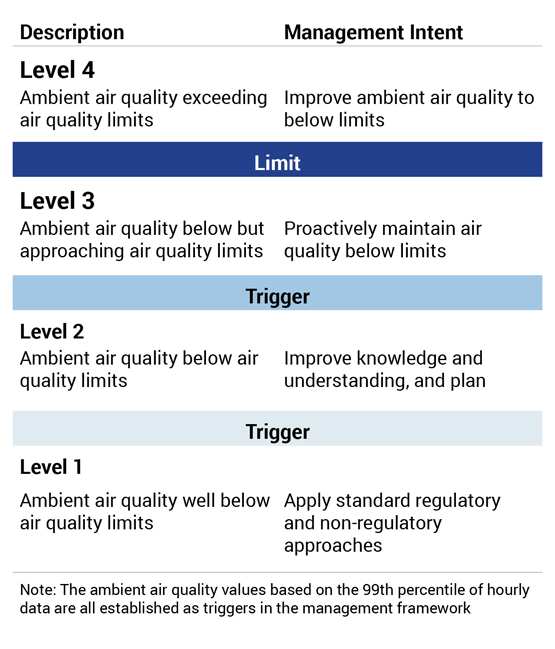
Air Quality Health Index
Alberta’s Air Quality Health Index—AQHI—is a scale created to help individuals better understand the impact of air quality on their health by providing important ambient air data at a glance. AQHI helps the public make informed decisions to protect their health by limiting short-term exposure to air pollution and adjusting activity levels during increased levels of air pollution. The WBEA reports AQHI ratings from nine of its continuous monitoring stations in the Wood Buffalo region.
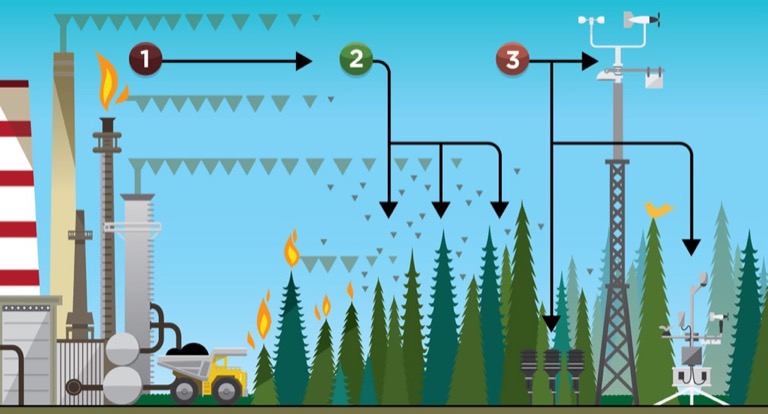
Primary compounds measured and used to calculate the AQHI are nitrogen dioxide (NO2), fine particulate matter (PM2.5), and ground-level ozone (O3)—all of which can negatively impact an individual’s respiratory system.
As an additional precaution, AQHI hourly pollutant concentrations are also compared against Alberta’s Ambient Air Quality Objectives (AAAQOs). If an exceedance is detected by the province, the AQHI will report a HIGH or VERY HIGH ambient air risk value.
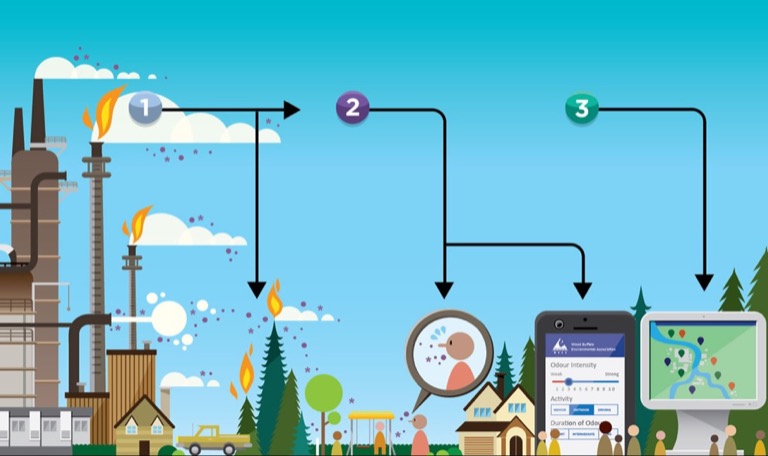
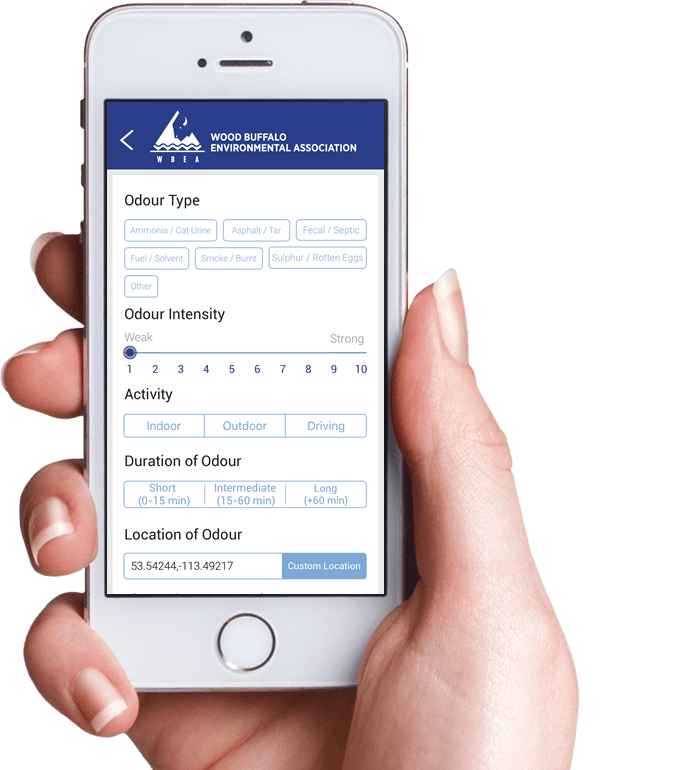
While the AQHI network relies on WBEA ambient air data, odour causing compounds measured in the network are not considered, therefore index data does not describe the potential for odour events.
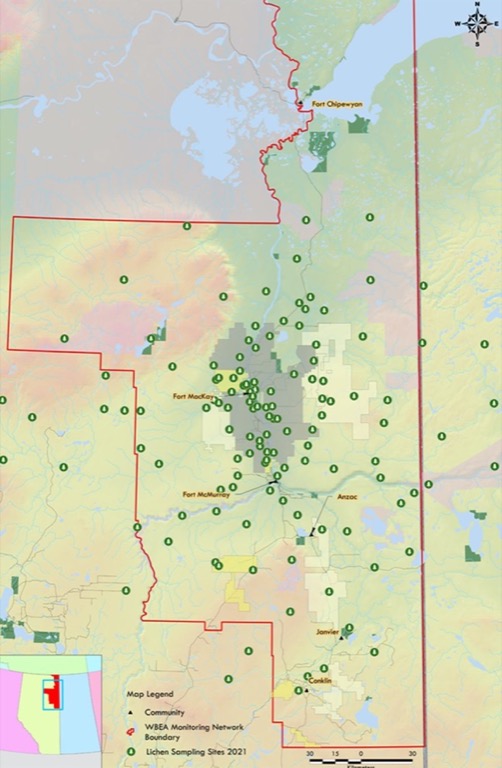
The community of Fort McKay has also developed its own Fort McKay Air Quality Index (FMAQI), based on the data collected by the WBEA at its Bertha Ganter-Fort McKay air monitoring station. The FMAQI is independent of the provincial AQHI, and includes compounds that can indicate odours, such as Total Reduced Sulphur (TRS), total hydrocarbons (THC), and sulphur dioxide (SO2).